Florida Closing Cost Primer for Buyers

Closing costs are inevitable when you’re buying or selling a property. While they vary from state to state, the amount you’ll pay in Florida depends on both the property and the county it sits in. As a buyer, you’ll have to cover most of the fees and taxes. In Florida, you’ll also have to post a fee for documentary stamps (or doc stamps), which is a percentage of the sales price. Then there are the taxes. You’ll likely be subject to property and transfer taxes.
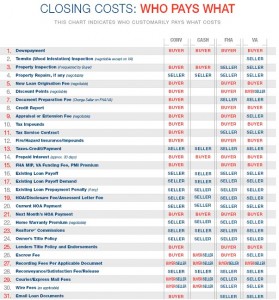
Neither party is responsible for 100% of the closing costs in Florida, which includes fees, taxes, insurance costs and more. The buyer typically pays between 3% to 4% of the home loan’s value and is responsible for the bulk of the fees and taxes. The seller usually pays between 5% to 10% of the home’s sale price. Closing costs also vary among counties.
Condos are regulated by the Florida Condominium Act. The legislation lays out your rights to the property and gives you an “undivided interest” in all the common areas of the building. You’ll have to pay a monthly maintenance fee or a yearly homeowners association fee to cover the servicing of those areas that fall under the “undivided interest.” The fee isn’t tax-deductible.
If you are getting a mortgage The fees shown on the Good Faith Estimate can be difficult to understand but can be broken down into five sections.
One-time fees
- Appraisal fee
- Reinspection fee
- Credit application, credit report and credit supplement fees
- Mortgage origination fee
- Lender’s title insurance policy (optional owner’s title insurance)
- Escrow fee
- Home inspection fee (optional)
- Closing attorney fee
- Courier fee
- Bank processing fee
- Recording fee
- Notary fee
- Loan discount points
Recurring fees
- Homeowners insurance
- Property taxes and tax servicing fees
- Mortgage insurance premiums
- Flood certification fee (in some areas)
Appraisal fees
Lenders typically require an appraisal as part of the underwriting process, before financing a home purchase. Appraisals will vary in price depending on the location and size of the property. The lender hires an appraiser to provide the fair market value of the home, and the buyer pays the lender.
Mortgage origination fee
Every lender will charge a mortgage origination fee, which covers their service and administrative costs. The average loan origination fee is 1% of the total loan amount. Buyers should shop for lenders with both experience and low origination fees.
Title insurance policy fees
Lenders typically require borrowers to purchase insurance to protect the financial institution from future title claims. This policy is called lender’s title insurance and the cost depends on the location and size of the property.
Owners title insurance protects the Buyer from future claims against the title. The customary party that pays for the Owners Title Policy varies by County in Florida. In Sarasota,Collier, Miami-Dade and Broward County, the Buyer pays for title insurance and chooses the title company. In all other counties, it is the Seller’s responsibility.
Escrow fees
During the purchase and sale transaction, your funds will enter a holding account managed by a third party — an escrow company. When the transaction is complete, the escrow representative will disperse your down payment, fees, and loan proceeds to the appropriate individuals.
Home inspection fee
A home inspection is a common contingency for a home purchase. As the buyer, you can hire an inspector to evaluate the condition of the home and its systems prior to purchase. Home inspection costs vary depending on the size and age of the property. You will pay the inspector for their service out-of-pocket, and this amount is separate from the purchase and sale transaction.
Attorney Fees
Florida is a Title Theory state and does not require that an attorney be used to close a real estate transaction. Private real estate attorneys, or borrower’s attorneys, are an additional and optional cost for buyers who want a specialist to assist them with contract-related issues or professional advice beyond the scope of their agent’s abilities. Private real estate attorneys charge by the hour or charged a fixed rate for the transaction and rates vary based on their level of expertise and services provided.
Documentation fees
During a financed home purchase, several institutions need to process information and create official records.
- The courier fee allows lenders to send your documents to necessary parties
- The bank processing fee pays the bank for handling the necessary loan documentation.
- The lender uses the recording fee to pay the county to file a public record of the transaction.
Loan discount point fees
When locking your interest rate with your lender, you’re allowed to buy down the rate. To do this, you pay “points” — essentially, paying interest in advance. One point is equal to 1% of the loan; but that does not translate to a 1% drop in interest rate. Not all buyers choose to buy down their interest rate, but when they do, the rates vary by lender.
Homeowners’ insurance
As a stipulation of your financing, you will be required to purchase homeowners’ insurance. You will continue to pay the insurance premium on a yearly or twice-yearly basis directly to your insurer, or monthly via an escrow payment that is part of your monthly mortgage payment to your loan servicer. Homeowners insurance policy fees range based on the amount of coverage and the size of the property.
Property taxes
Your property taxes will be prorated based on your closing date. Some buyers pay their taxes in lump sums annually or biannually. If you don’t pay this way, you might escrow the taxes, which means they would be included as an escrow line item in your monthly mortgage payment to your loan servicer. Property taxes are paid in arrears in Florida.
Mortgage insurance premiums
If your loan amount is more than 20% of the value of the home, you are typically required to pay insurance to protect your lender’s investment. Mortgage insurance is generally escrowed but may vary from lender to lender. Some lenders will also charge a one-time application fee for mortgage insurance.
Flood insurance
Depending on the location of your property, you may also be obligated to purchase flood insurance to help protect your lender’s investment. Flood insurance policies range by risk level, based on location and are a Federal Program and the pricing cannot be competitively shopped for.
What are the closing costs for cash buyers?
Cash buyers are still required to pay for things like notary fees, property taxes, recording fees, and other local, county and state fees. Unlike a buyer who is using financing, cash buyers won’t have to pay any mortgage-related fees. But most cash buyers still opt to pay for things like appraisals, inspections, and owner’s title insurance.
Closing costs can vary depending on where you live in Florida, the type of property you buy and how much it sells for. While the seller forks over some money, the buyer pays for the bulk of the fees and taxes, which typically add up to 2.5% of the average sale price depending on the time of year you close ( proration sensitive).







 Kim N. Bregman
Kim N. Bregman