Keeping Home Buyers Safe During COVID-19 Pandemic


Serving South Florida


Filed under: Blog, Boca Raton real estate, coronavirus, COVID-19, Exclusive Buyer Agency, Exclusive Buyer Agent, First Time Homebuyers, Florida Real Estate, Home Buyer Advice, Home Buyers, home safety, Homebuyer Advice, House Closings, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, Real Estate Investment, real estate news, Relocation, South Florida Real Estate by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on Keeping Home Buyers Safe During COVID-19 Pandemic

Rates are lower than ever; when a refinancing is done right, it can save you thousands of dollars. But not every potential refi makes the cut. Sometimes the expenses just don’t justify the potential savings.
It is time to refinance your home mortgage if the terms lower your mortgage interest rate, pay off their mortgage years earlier, or saves thousands in interest over the life of the loan. You can save serious money by refinancing your mortgage. But due to refinancing fees and expenses, not every refi makes financial sense.
COVID-19 is creating changes with lenders and how they are doing business. This is resulting in refinancing taking longer and getting stricter than it has been in the past. Although the mortgage process is considered essential as a financial transaction, depending on where you live, there may be changes related to COVID-19 involving your appraisal, rate lock and closing process.
Rates are quite low and because your home is your biggest financial investment, the equity can be very useful as a resource in times of trouble. But if you’re thinking of financing your home loan there are several steps you should take to make sure that it’s the right move for you.
How Long Do You Plan On Being In Your Home?
Being able to answer this question will help you figure out the term length you want on any refinanced mortgage; but there’s another reason asking this question …
If you plan on moving within the next 5 – 10 years, it could be worth your while to look at an adjustable rate mortgage ( ARM). You get a lower rate initially with an ARM because the rate can adjust after the teaser period. But if you move before the end of the fixed-rate time frame, you don’t have to worry about whether the rate is going up and down in the end. Additionally, your payment will tend to be lower because most adjustable rate mortgages are based on 30-year terms.
Age Of Current Loan
The age of your current loan sometimes plays a role in whether you can refinance. Even if you can refinance, it does not always make sense. When you refinance you have to pay closing costs. If you are not planning on staying in the house past the breakeven point when the savings and the additional expenses paid starts to net to overall reduced costs for home ownership, the it is not the time to refinance. You may want to accelerate buying a new home to realize the saving from lower interest rates.
Plans For Monthly Savings
If you determine that you’re going to save money by refinancing based on the rate and term you can get, make sure that you have a plan for what you’re going to do with the monthly savings in order to put yourself in a better financial position. No one knows exactly when COVID-19 is going to end and how long it will take for the economy to recover. If you can save money now, you can work on establishing the savings need should the vaccine be delayed or we continue with a longer recession
You could use your savings to build up an emergency fund. Maybe you choose to allow yourself to save money in the future by paying off high-interest debt now. You can also use this to catch up on saving for retirement if you stopped contributing temporarily while dealing with the situation caused by the virus.
It’s a very volatile market right now, so we advise all of our clients to rely on the advice of their Home Loan Expert and Financial Advisors at all times.
The Mortgage Refi Process
Approving a mortgage is a complicated process, one that requires a lender to validate a borrower’s income, check the value of the home being used as collateral and scrutinize the title history of the property.
Just as refinancing applications picked up, the coronavirus pandemic dramatically changed the way everyone in the mortgage industry works. Loan officers no longer go to the office. Appraisers stopped walking through houses. And no one gathers around the title company’s closing table. The process is a little slower because everybody’s working from home right now. Things that would take an hour to do are taking a day sometimes.
It is more difficult to verify a borrower’s employment. A task once dispatched with a quick call to the borrower’s human resources department now means leaving a voicemail and waiting a day or two for a response.
Meanwhile, homeowners looking to refinance may have to get in line behind buyers who need a mortgage so they can close on a house which are a priority with lenders.
The mortgage industry already had been digitizing, and lenders quickly adapted to many changes. One stumbling block, though, is that most lenders still require some documents to be signed in the presence of a legal witness and notarized. Florida allows for mobile notaries and they are busier than ever.
Sometimes, documents are being signed remotely and online and mobile notaries are not allowed yet. You need to allow time for in person notarization and overnight mailing of documents. Digital closings may be the way of the future, but we are not there yet.
What You Can Do to Secure a Smooth Refinance
Here are a few ways you can make the refi process as smooth as possible:
— Get your paperwork in order. Don’t let something simple like a missing document delay your refinance. Collect PDFs of financial documents, including pay stubs, bank statements, tax returns and retirement accounts.
— Make sure the lender will honor your rate lock. In normal times, lenders extend rate locks for 30 to 60 days, meaning you won’t have to pay more if rates go up before your loan closes. These aren’t normal times, though, and many refinances aren’t closing within 30 to 60 days, so make sure your lender is willing to extend your rate lock if your deal is delayed.
— Keep your credit score tight. Now isn’t the time to miss a payment, take on new debt or otherwise do anything to lower your credit score. Lenders are being especially strict about borrowers’ credit histories.
Filed under: Blog, Boca Raton real estate, coronavirus, COVID-19, Exclusive Buyer Agency, Exclusive Buyer Agent, Florida Real Estate, Home Buyer Advice, Home Buyers, Home Financing, Homebuyer Advice, Mortgage Information, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, Real Estate Investment, real estate news, Refinancing, South Florida Real Estate by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on Should You Refinance During The COVID-19 Situation?
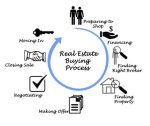
Filed under: Blog, Boca Raton real estate, coronavirus, Exclusive Buyer Agency, Exclusive Buyer Agent, First Time Homebuyers, Florida Real Estate, Foreign Home Buyers, Home Buyer Advice, Home Buyers, Home Financing, home Inspections, home safety, Homebuyer Advice, House Closings, International Home Buyers, International investors, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, Real Estate Investment, real estate news, Relocation, South Florida Real Estate by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on COVID-19 Real Estate Home Buying Process

The novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has put a stop to the normal routines of everyday life both in the U.S. and abroad. And while social distancing is the course of action to take until told otherwise, moves aren’t always something that can wait. Real estate is considered an essential service in all states and there are many services providers to assist you in facilitating a move to a new home.
By taking extra safety precautions and minimizing social contact, you can still move safely. If you are about to move, you can still pull it off with a little extra planning and a few precautionary steps.
Here are some tips for making your move as safe, seamless and stress-free as possible.
There have not been any notable shutdowns of service among major moving companies. That being said, decisions about closures may be left to individual franchise owners. If you have already scheduled your move and haven’t heard anything, assume that your moving company is still providing services unless told otherwise, but still call just to confirm.
If you’re worried about moving during a pandemic for a move that is still upcoming and for which you haven’t scheduled movers, it’s hard to say what will and will not be available in the months to come. For now, continue to do research on companies and ask directly what steps are being taken when you reach out. What has changed at this point is largely going to be related to the customer experience itself, including frequent hand washing among movers and no physical contact between movers and clients.
If you need to select a moving company, ask for a virtual quote and see if the company offers fully contactless service. Forgo handshakes, for obvious reasons. A smile and a generous tip (sent through Venmo, PayPal or another contactless digital platform) are a welcome substitute. These companies have virtual estimate procedures available for competitive quotes
Moving companies are taking the coronavirus pandemic very seriously. To that end, companies across the country have put into place protocols designed to protect their employees and their customers. These include:
All of these practices help ensure that moving services can remain available in a safe way.
| Company | Status | Additional info |
| AmeriFreight | Open | Learn more |
| Montway Auto Transport | Open | Learn more |
| Sherpa Auto Transport | Open | Learn more |
| Ship a Car Direct | Open | Learn more |
| uShip | Open | Learn more |
| Company | Status | Additional info |
| Allied Van Lines | Open | Learn more |
| American Van Lines | Open | Learn more |
| Expedia Van Lines | Open | Learn more |
| First National Van Lines | Open | Learn more |
| International Van Lines | Open | Learn more |
| Interstate Moving & Relocation Group | Open | Learn more |
| North American Van Lines | Open | Learn more |
| PODS | Open | Learn more |
| Silver Star Moving Group | Open | Learn more |
| United Van Lines | Open | Learn more |
Same as moving companies, major storage companies continue to run operations. What you might be able to expect however is limited hours of accessibility and/or a reduction in the number of customers who are able to access their units at any one time. Storage companies should also be following proper hygiene practices, including sanitization of access pads and the requisite six feet or more of space between customer and customer and customer and employee.
| Company | Status | Additional info |
| CubeSmart | Open | Learn more |
| Extra Space Storage | Open | Learn more |
| Public Storage | Open | Learn more |
The process of a DIY move looks pretty much the same now as it did before COVID-19, minus the ability to have a couple friends come over and lend a hand in exchange for pizza. Some additional things that you will want to do however include keeping hand sanitizer, soap, and paper towels accessible at all times, we well as making a detailed plan for both your departure and arrival.
Major rental truck companies continue to be in service, as they are considered essential for transportation and personal mobility needs. Again, what may be different is the experience, since companies like Enterprise and U-Haul have put into place their own protocols for physical distancing. This means that your pick-up and drop-off location may not be at the branch office, and that you’ll have to make your reservation online or over the phone instead of in person.
If you rent, talk to your current landlord about how you can safely drop off keys and collect your security deposit, and talk to your new landlord about the process for a safe move in. Putting in a blueprint of steps ahead of time will help you maintain social distancing during your DIY move and answer any questions you might have about the process.
| Company | Status | Additional info |
| Budget | Open | Learn more |
| Enterprise | Open | Learn more |
| Penske | Open | Learn more |
| The Home Depot | Open | Learn more |
| U-Haul | Open | Learn more |
One silver lining is that social distancing means that you might have more time to devote to organizing your home prior to your move and getting rid of the things you no longer want or need. If you plan on donating items like clothing, linens, furniture, shelf stable non-perishables, etc., call the place that you would like to donate to ahead of time and see what their policies are. While many people are in need during this time, it’s likely not going be quite as easy as just driving to your nearest donation center and dropping stuff of (but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t do it).
| Company | Status | Additional info |
| 1-800-GOT-JUNK | Open | Learn more |
| College Hunks Hauling Junk | Open | Learn more |
| LoadUp | Open | Learn more |
| Waste Management Dumpster Rentals | Open | Learn more |
This is important to confirm your reservation and discuss best practices for moving day. Moving companies are putting in lots of safeguards to help protect their clients, and it helps to be on the same page as them in terms of what is expected.
You are going to want to get it right with just one trip to the store, so make sure you know exactly what you’re going to need for your move. Don’t use free or recycled moving boxes. The coronavirus can live on cardboard for as long as 24 hours, so now is not the time to be picking up free moving supplies from places that are recycling them. Boxes that you already have in your home are fine, but if you need any extras then you’ll need to go to the store and buy them new (even better if you can then purchase them through self-checkout). Better yet, order all your moving supplies online and have them shipped to your residence. Clean as you pack. Use this opportunity to sanitize your belongings, wiping items down with disinfectant. If you don’t have any, you can make one with a solution of one tablespoon bleach to one gallon of water.
Coronavirus can last a long time on surfaces, including up to 24 hours on cardboard boxes. Your movers will be wearing gloves, but for everyone’s safety you should still have your boxes packed and sitting untouched at least a day before your movers arrive.
To aid your movers in following necessary hygiene practices, be sure to leave out products that they can use while they transport your items to and from the moving truck. That includes soap and paper towels by the sink, and hand sanitizer by the door that they’ll be entering and exiting through. If you’re concerned about having enough supplies, let your moving company know so they can be sure to bring them along for use during the move.
In advance of your move, reach out to your neighbors — especially if you live in an apartment building — and share the date and time you plan to move. This gives everyone in your direct vicinity an opportunity to avoid unnecessary contact and let you know if your timing is a problem.
Be sure to deep clean and sanitize your new home before you move into it. Here are a few resources and tips to help:
CDC’s recommendations on how to clean and sanitize your home
If you have an extra minute, here are some additional things to consider
Additional resources:
Moving is stressful under the best of circumstances; this is a scary time and certainly takes moving stress to the next level. With some planning and organization, you can relocate and stay safe even in an environment with a pandemic.
Filed under: Blog, Boca Raton real estate, coronavirus, Down Sizing, Exclusive Buyer Agency, Exclusive Buyer Agent, First Time Homebuyers, Home Buyer Advice, Home Buyers, home safety, Homebuyer Advice, House Closings, International Home Buyers, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, real estate news, South Florida Real Estate by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on Guidance for Moving During COVID-19

|
|
Filed under: Blog, Boca Raton real estate, contracts, coronavirus, Exclusive Buyer Agency, Exclusive Buyer Agent, First Time Homebuyers, Florida Real Estate, Home Buyer Advice, Home Buyers, Home Financing, home Inspections, Homebuyer Advice, House Closings, Mortgage Information, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, real estate news, South Florida Real Estate by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on Virtual Home Buying Made Easy!

FIRPTA (Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act) Withholding is the Withholding of Tax on Dispositions of United States Real Property Interests
The disposition of a U.S. real property interest by a foreign person (the transferor) is subject to the Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act of 1980 (FIRPTA) income tax withholding.
FIRPTA authorized the United States to tax foreign persons on dispositions of U.S. real property interests.
Persons purchasing U.S. real property interests (“transferee”) from foreign persons, certain purchasers’ agents, and settlement officers are required to withhold 15% of the amount realized.
Withholding is intended to ensure U.S. taxation of gains realized on disposition of such interests. The transferee/buyer is the withholding agent. If you are the transferee/buyer you must find out if the transferor is a foreign person. If the transferor is a foreign person and you fail to withhold, you may be held liable for the tax.
One of the most common exceptions to FIRPTA withholding is that the transferee (purchaser/buyer) is not required to withhold tax in a situation in which the purchaser/buyer purchases real estate for use as his home and the purchase price is not more than $300,000. However, buyers should be aware that while they may meet the withholding exemption they are still responsible for the seller’s tax liability, interest and penalties should the seller not file a US income tax return to report the sale and pay any relevant taxes.
Note to Non-Resident Buyers – If you purchase property from a non-resident seller and an exception to FIRPTA withholding does not apply then you must ensure that FIRPTA is satisfied as part of the closing. Check your settlement statement prior to closing where you should see 15% of the sales price withheld on the seller’s side of the settlement statement. Request a copy of the withholding certificate from the closing agent and, if withholding was calculated, request a copy of forms 8288, 8288-A and front and back of cancelled check. Retain these documents in a safe place along with your settlement statement and other closing documents.
Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act (FIRPTA) Withholding
U.S. Tax law requires that a non-resident alien who sells an interest in U.S. real property is subject to withholding, for tax purposes, of 15% of the gross sales price (i.e. $45,000 on a property with a sales price of $300,000). The withheld amount is required to be forwarded to the IRS, by the Closing Agent, within 20 days of the date of closing. These funds are held until the IRS is satisfied that all taxes due by the non-resident are paid. In order to apply for a refund you can either:-
File U.S. tax returns for each year that rental income was received, reporting all income and expenses; file a final U.S. tax return in the year following the year of sale, to report the sale and recover the balance of cleared funds. This process can take up to eighteen months depending on when, during the tax year, the property is sold.
File prior year tax returns (where required) plus an application for early release of cleared withholding on or before the date of closing. By making this submission, the 10% withholding remains with the Closing Agent whilst the IRS processes the Withholding Application and issues a Withholding Certificate for the cleared funds – usually around 90 days.
Please note that applying for and receiving a Withholding Certificate does not eliminate your requirement to file a final U.S. income tax return to report the sale transaction. In fact, when your final tax return is filed you may receive a further tax refund depending on the number of owners and length of time that the property was held.
In order to ensure a timely release of your funds it is extremely important that the following is obtained PRIOR to closing:-
Buyer’s names, address and SSNs – if U.S. Citizens
Buyer’s names, address and ITINs – if non residents
Or, if the buyers are non residents and do not have ITINs, the buyer’s completed Form W-7 (one per buyer) and authenticated copy of the picture page of their passport(s)
Without this information the Application for a Withholding Certificate and early refund will be rejected. We suggest that you request your Realtor prepare your sales contract contingent upon the buyers providing the above information.
Who’s responsible for FIRPTA withholding on the sale of U.S. property?
Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act (FIRPTA) was established in 1980 to ensure the withholding of estimated amount of taxes which may be due on the gain from the disposition or transfer of a U.S. real property interest from a foreign person.
If you purchase U.S. real property from a foreign individual or corporation then you are required to make sure that the seller pays any taxes due on the property. The buyer must execute or have executed the correct forms including the sellers name, address and social security number or individual taxpayer identification number. 15% of the gross sales price must be withheld and submitted to IRS or held in escrow whilst an application for reduced FIRPTA withholding is timely filed and processed.
If the buyer does not take care of the withholding and the seller is a foreign entity who leaves without paying their tax then 15% will be taken from the buyer.
Most buyers are unaware that it is their responsibility to determine if the transferor/seller is a foreign person and subject to FIRPTA withholding. In reality, the settlement agent (Title Company or Attorney) may be instructed to deduct the 15% and submit to IRS or hold in escrow whilst an application for reduced FIRPTA withholding is submitted to IRS for processing.
Filed under: 20 Blogs, Blog, Boca Raton real estate, Exclusive Buyer Agent, First Time Homebuyers, Florida Real Estate, Foreign Home Buyers, Foreign Nationals, Home Buyer Advice, Home Buyers, Homebuyer Advice, House Closings, International Home Buyers, International investors, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, Real Estate Investment, real estate news, Real estate trends, South Florida Real Estate, Tax deductions by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on FIRPTA Withholding – Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act

Any responsible buyer wants to know everything about the home they’re buying before signing on the dotted line. After all, this is probably the biggest purchase you will ever make, so due diligence is a must. The majority of the real estate agents in Florida are Transactional Agents and do not owe the Buyer a fiduciary duty, An Exclusive Buyer Agent does and will work for the buyer to determine all the information known about the property and advise you on inspections, permit searches, etc. Reviewing the Seller’s Disclosure is the first step in this process.
A Seller’s Disclosure in the State of Florida Is a standard form that is essentially a checklist in which a seller indicates the condition of the different features of a property, any known problems affecting the property, and any pending legal issues. This could include things like knowledge of lead-based paint, water damage, pest damage, past repairs, past insurance claims, any history of property line disputes, etc.
Typically, a seller’s disclosure form is filled out by the seller along with their listing paperwork. When buyer’s agents go into the Multiple Listing Service (MLS) to look up potential properties for their clients, that disclosure statement should be available or can be requested from the listing agent.
I am increasingly running into situations wheretransactional brokerage firms are taking the position that since a Seller’s Disclosure is NOT required by law that are not asking the sellers of their listings to fill one out. The first line of the SPDR provides “Notice to Licensee and Seller”; the less they know, the easier it is to make a “deal”. They are relying on the fact that other transactional agents working with buyers will feel the same and not ask for a Sellers Disclosure.
Although sellers aren’t required to complete this specific SPDR form, a residential seller does have to comply with the rule established in Johnson v. Davis. In that case, the Florida Supreme Court held that “where the seller of a home knows of facts materially affecting the value of the property which are not readily observable and are not known to the buyer, the seller is under a duty to disclose them to the buyer.” These material facts are sometimes referred to as latent defects. In addition, in Rayner vs. Wise Realty Co. of Tallahassee, the First District Court of Appeal provided that this same disclosure requirement applies to residential properties that are being sold as is.
In cases were the listing agent does not provide a Sellers Disclosure I request that the Seller answer all my questions in writing and provide a comprehensive list of questions that encompasses everything asked on the SPDR and more.
A seller’s disclosure form is NOT a substitute for a home inspection. Remember, sellers are required to disclosure only problems they know about. Most homeowners don’t go in their attic very often, and have probably never been up on their roof, and they aren’t required to do so before filling out the disclosure. While this document can provide a lot of valuable information, the home inspection is another layer of protection for a buyer.
The importance of this disclosure statement is just one of the many reasons why it’s critical for buyers and sellers to use an Exclusive Buyer Agent ( EBA) during any real estate transaction. EBAs are up-to-date on the latest laws and regulations and are very experienced with the complex documents and paperwork. They can help walk buyers through the disclosure so they understand all aspects of the home they’re buying and recommend the appropriate home inspections ( WDO, Radon, Leak Testing, Mold, and more) to ensure that any hidden defects are found in advance of the purchase.
Filed under: Blog, contracts, Exclusive Buyer Agent, First Time Homebuyers, Florida Real Estate, Home Buyer Advice, Home Buyers, home Inspections, Homebuyer Advice, House Closings, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, Real Estate Investment, real estate news, Real estate trends, South Florida Real Estate, Uncategorized by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on What Home Buyers Can Learn From a Seller’s Disclosure Statement

|
|
|
World events are conspiring to make it more expensive for you to borrow money to buy a house.
Mortgage rates have increased for six consecutive weeks, according to Bankrate data, bringing interest on a 30-year fixed rate loan to 4.44 percent—the highest level in 11 months—while home prices continue to rise due to a lack of available homes.
After years of tepid economic growth, inflation and wage growth recently found a groove, while the Federal Reserve’s plan to raise short-term interest rates multiple times for a consecutive year has reduced the value of government debt.
Homebuyers Should Get off the Fence
Mortgage rates are moved by the yield on 10-year Treasuries, rather than short-term rate hikes by the Fed. That’s why mortgage rates fell throughout 2017, for instance, even as the central bank raised the federal funds rate three times. Rates remain cheap, however, compared to historical prices. A 30-year fixed-rate mortgage came with an interest rate above 6 percent just before the Great Recession in 2007. Potential homeowners should get off the fence and make a bid, assuming you have an affordable home target and adequate savings, because rates are likely only heading north.
Mortgage rates are expected to climb in 2018, so it might be worth shopping for a mortgage before this long period of low rates takes a turn.
Here are several predictions from the largest housing and mortgage groups for the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage:
|
Filed under: Blog, Exclusive Buyer Agent, First Time Homebuyers, Florida Real Estate, Home Buyers, Home Financing, Homebuyer Advice, House Closings, International Home Buyers, International investors, Mortgage Information, Mortgage Interest Deductions, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, Real Estate Investment, real estate news, Real estate trends, South Florida Real Estate by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on Why Your Mortgage Is Getting More Expensive

Filed under: Blog, Exclusive Buyer Agent, First Time Homebuyers, Florida Real Estate, Foreign Home Buyers, HELOC deductions, Home Buyer Advice, Home Buyers, Home Financing, Homebuyer Advice, House Closings, Mortgage Information, Mortgage Interest Deductions, Real Estate, Real Estate Closings, Real Estate Investment, real estate news, Relocation, Retirement, South Florida Real Estate, Tax deductions by Kim Bregman
Comments Off on Tax Deductions to Take in 2017 Before They Disappear
 Kim N. Bregman
Kim N. BregmanAll information is provided by the licensed REALTOR®/Broker/Agent. This information is not verified for authenticity or accuracy and is not guaranteed. This website is not responsible or liable in any manner for any content posted herein or in connection with our services. Information is not guaranteed and must be confirmed by the end user.
Copyright © 2026 OPTIMA PROPERTIES. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy | Intellectual Property Rights | Sitemap | Real Estate Website Design & Internet Marketing by Agent Image